The Engine of Customer Centricity: Understanding Modern CRM Software Today
In today's hyper-competitive business landscape, the customer is the undisputed king. The technology that empowers businesses to manage and nurture their relationships with these customers is known as CRM Software, or Customer Relationship Management software. It is a powerful platform that acts as a centralized database for all customer interactions, providing a single, unified view of every prospect and client. From sales and marketing to customer service, CRM software streamlines processes, improves communication, and provides the data-driven insights needed to build stronger, more profitable, and longer-lasting customer relationships. The CRM Software Market Is Projected To Reach a Valuation of USD 153.35 Billion By 2035, Reaching at a CAGR of 11.50% During 2025 - 2035, highlighting its indispensable role as the central nervous system of any modern, customer-centric organization. This growth reflects its critical function in today's digital-first business environment.
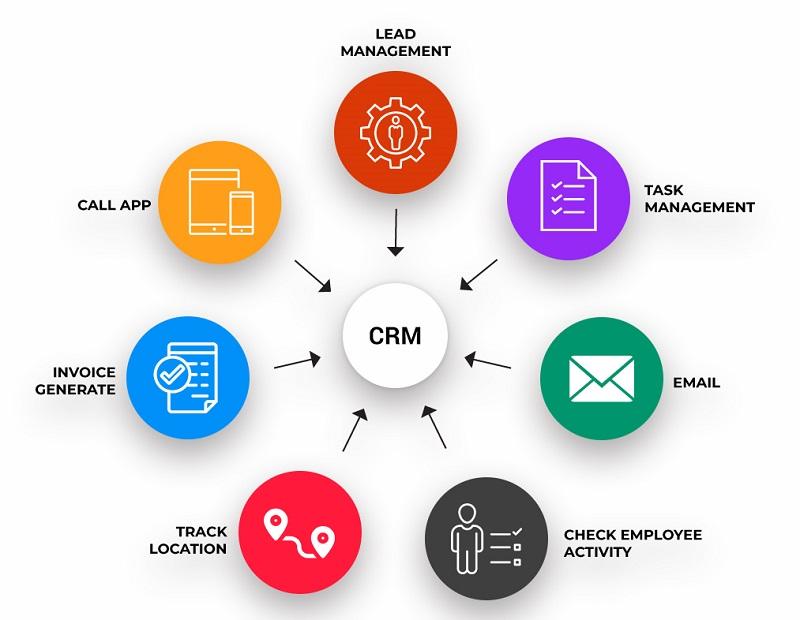
The core function of CRM software is to break down the information silos that traditionally exist between different customer-facing departments. In a pre-CRM world, the sales team had their own records, the marketing team had their own lists, and the customer service team had their own ticketing system. This fragmentation led to a disjointed and often frustrating customer experience. CRM software solves this by creating a single, shared record for every customer. This "360-degree customer view" includes their contact information, a complete history of all their interactions with the company (emails, phone calls, support tickets), their purchase history, and any other relevant data. This ensures that anyone in the organization who interacts with a customer has the full context of that relationship, enabling more personalized and effective communication.
CRM software is typically organized around three main pillars: sales, marketing, and service. Sales CRM, or Sales Force Automation (SFA), provides tools for managing leads, tracking opportunities through the sales pipeline, forecasting revenue, and automating repetitive sales tasks. This helps sales teams be more organized, efficient, and effective at closing deals. Marketing CRM provides tools for running marketing campaigns, segmenting customer lists for targeted messaging, automating email marketing (marketing automation), and tracking the ROI of marketing spend. Service CRM provides tools for managing customer support inquiries, typically through a ticketing system, and for building a knowledge base of common issues and their solutions. This helps service teams resolve issues faster and improve customer satisfaction.
The benefits of implementing a CRM system are profound and impact every part of a business. It leads to increased sales productivity by allowing salespeople to focus on selling rather than administrative tasks. It improves marketing effectiveness by enabling highly targeted and personalized campaigns. It enhances customer loyalty and retention by providing faster and more informed customer service. Furthermore, the wealth of data captured in a CRM system provides invaluable insights for senior management, allowing them to spot trends, understand customer behavior, and make more strategic, data-driven decisions about the future direction of the business. In essence, CRM software is not just a tool; it is a business strategy focused on putting the customer at the center of everything.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Autre
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness